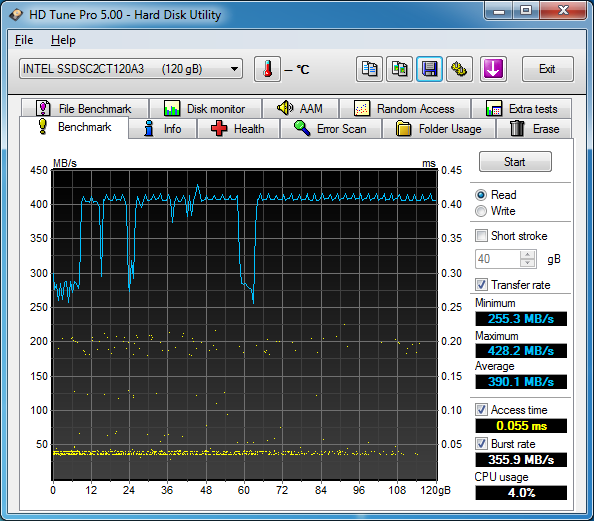
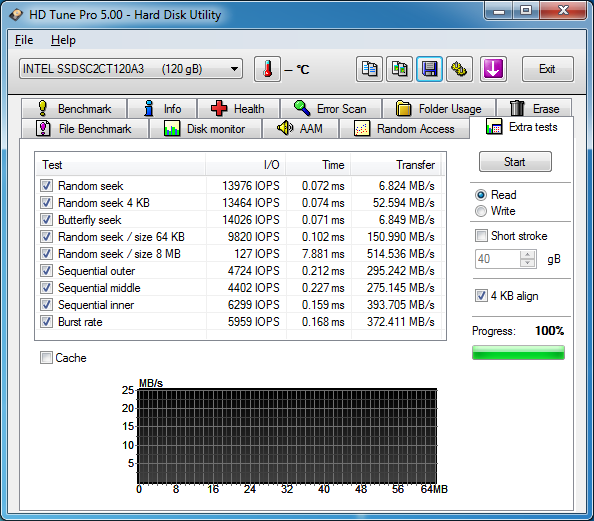
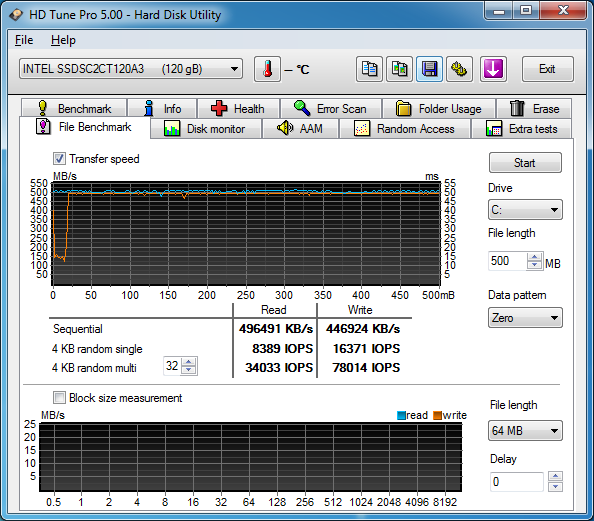
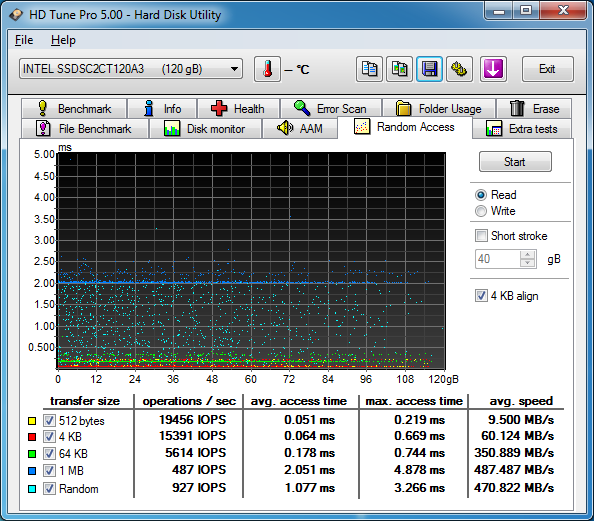
There are many reasons you may be using an SSH port other than 22; perhaps you changed it as a security measure, or perhaps you have multiple machines behind your firewall which you are port forwarding to and thus have to use other ports in addition to 22. Rsync is an extremely powerful file synchronization tool which by default uses SSH to connect your source and destination, thus if you have changed your SSH port you will need to tell rsync. This can be easily done with the e switch like so (using 2222 as the new SSH port as an example):
rsync -e “ssh -p 2222” /path/to/source [email protected]:/path/to/destination
As a practical example using the other options -avzP (our typical selection) your command might look like:
rsync -avzP -e “ssh -p 2222” /home/user/myfile [email protected]:/home/user/